What is Babesiosis?
Babesiosis is a microscopic parasitic disease, also called a tick-born disease, that infects red blood cells caused due to changes in human behavior and warmer weather. There are two main animals on which these ticks survive. These are mice and deer and people move to the areas and come in contact with these animals and act as hosts for the ticks. It has been very common in the northeastern and Midwestern United States since 2011 and increased significantly. Now Human babesiosis, the endemic disease, has spread to three new states named Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont, as reported by CDC.
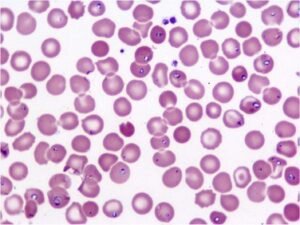
Etiology:
Babesia microti is spread by Ixodes scapularis ticks, commonly named black-legged or deer ticks. It is mainly spread by the young nymph stage of the tick. These nymphs are present in the warm season. Some people got infected after the transfusion of contaminated blood. New born baby may also get infected from his/her mother during pregnancy or delivery.
Babesiosis symptoms:
The symptoms of disease are varying as a decade and it took about a month to appear symptoms after the bite. If contaminated blood is infused then it would take 2 months to show symptoms. Moreover, healthy populations with babesiosis remain asymptomatic. People infected with babesiosis feel fatigued and hemolysis is detected as the parasite destroys the red blood cells. Common symptoms include sweating, chilling, and thrombocytopenia and these symptoms remain for several months.
Some other symptoms are following and vary from person to person.
Headache
Muscle Pain Anorexia
Nonproductive cough
Loss in weight
Mood swings
Depression
Nausea
Vomiting
Throat soreness
Redness in eye
Stomach pain
Fear from light
Enlargement in spleen and liver
Jaundice
In severe cases, high fever up to 40.5 °C (105 °F) occurs in patients with chilling and severe hemolytic anemia. Some people experience depression and organ failure.
In the United States, babesiosis in humans mainly occurs due to Babesia microti. Rodents act as primary hosts and deer ticks act as vectors. These rodents and deer are very native to people living in the US and easily transmit the parasite to humans. These parasites enter the bloodstream and infect the red blood cells by rupturing them causing hemolytic anemia.
A babesiosis smear is the microscopic examination of a blood sample infected with the parasite. This test is pursued for the confirmation of the disease. Giemsa or Wright stains are used to identify the infected red blood cells. At the initial stage, the rate of infection is less than 1%, so multiple smear tests are performed for confirmation.
Babesiosis treatment and prevention:
People should wear light-colored clothes while going out walking on the ground and in wooden areas. Clothes should be interlocked i.e. shirt should be tucked inside the pants and pants should be tucked inside the socks. Avoid areas having high grass. CDC recommends the washing of clothes with insect repellents or containing 0.5% permethrin, a common insecticide.
Infection on the skin is rare due to babesiosis disease. However, co-infection with babesia may affect the rashes on the skin that occur due to Lyme disease. Otherwise, no babesiosis rashes occurred due to this parasitic bite.
Treatments of babesiosis are available. People should confirm the correct diagnosis with testing from reputed clinical laboratory. Asymptomatic people need not require treatment. People that have confirmed the babesiosis disease should consult their health care adviser for proper medication.
Babesiosis treatment in ancient science:
Ayurvedic medicines were used from ancient times and they are believed to be effective and safe from childhood to adulthood. Herbal medicines are meant to be the treatment of disease from the root with no side effects. These medicines have taken longer time than the allopathic medicine system. Study shows that Garlic oil, Black pepper, and their constituents have a positive effect against babesiosis duncani on animal hamster models. These findings of herbal plants show that these plants have anti-parasitic activity. Many different studies show that herbal medicine extracts of Uncaria tomentosa, Stevia rebaudiana, Juglans nigra, Cryptolepis sanguinolenta, Artemisia annua, Andrographis paniculata, Dipsacus fullonum, Withania somnifera, Scutellaria baicalensis, and Polygonum cuspidatum have potential effect against babesiosis when study carried out on animal model. These extracts can be used for human beings once their clinical study is complete.
People Also Read: From Fingertips to Heartstrings: Embracing the Power of Touch, Healthy Sweetener Exchanger to Stay Disease Free
Conclusion:
Babesiosis is a disease that can be prevented by taking extra care when we go outside. Moreover, they mainly act upon red blood cells that affect our health system abruptly. By adding the herbs dictated above to our daily eating habits we can save ourselves from this dangerous disease. Rightly said that “prevention is better than cure”.
Image Source: Freepik

