Digestion is a process of breakdown of larger insoluble food particles into smaller soluble food particles readily absorbed in watery blood plasma. These small food particles are absorbed into the small intestine in the bloodstream. The breakdown process is known as catabolism and involves mainly two processes. One is mechanical digestion and the other is chemical digestion. Mechanical digestion involves physical breakdown starting with chewing (mastication) in the mouth and small intestine by contraction. In chemical digestion, digestive enzymes break down the food particles readily absorbed in blood plasma.
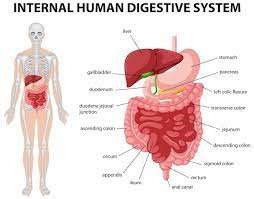
Easy to understand digestion definition:
The process of breaking down food material in the stomach so that the body can use it for energy, tissue growth, and repair of damaged cells.
Where does digestion begin?
In the process of digestion, food enters the human digestive system through the mouth, and mechanical digestion starts with chewing (mastication) and the wetting of food takes place with saliva. Saliva mainly contains salivary amylase where carbohydrate digestion begins in the presence of amylase that is secreted by salivary glands. Starch present inside the food is digested by salivary amylase. The food is lubricated by mucus present in the saliva. About 30% of starch is hydrolyzed in the mouth. Mastication and starch digestion collectively convert the food material into a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. Food will move down to the esophagus and into the stomach by peristalsis, a process of coordinated muscle contraction that occurs automatically to move food into the digestive tract. The stomach contains gastric juice, hydrochloric acid, and pepsin for further breakdown of food particles. Rennin is also present in the stomachs of infants and toddlers along with above said juices to digest milk. Pepsin breaks down the proteins into peptides or proteoses in the small intestine in chemical digestion and is further converted into dipeptides and amino acids by enzymes.
How long does digestion take?
Digestion time is different for different people and varies among the sexes and kids. It could take six to eight hours after you eat the food to reach the small intestine from the mouth through the stomach. Food then enters the large intestine for further absorption and elimination of undigested food material in the form of feces. It takes about 36 hours to cross the entire large intestine. In short, it took 3-5 days to eliminate the waste of undigested food in the form of feces from the food entered into the mouth. Junk foods delayed the digestion time. This lifestyle change impacts our bodies adversely.
Where does protein digestion begin?
Protein is the most important component required for muscles, hair, eyes, organs, and hormones. Moreover, enzymes are also made up of proteins. It helps in repairing old tissue and developing new ones. Proteins are made up of 20 amino acids and out of 20 amino acids, 11 are prepared by the body itself. The remaining 9 amino acids are taken by the body from the outside with food and these 9 amino acids are called essential amino acids. All essential amino acids are present in protein source foods like milk products, fish, meat, eggs, nuts, beans, and seeds.
Protein digestion begins as we chew the food inside the mouth. Amylase and lipase are the two enzymes present in saliva and responsible for the breakdown of carbohydrates and fats. Hydrochloric acid and enzyme proteases further break the amino acids once food reaches the stomach. These tiny particles of amino acids are absorbed in the small intestine which contains microvilli. These microvilli allow maximum absorption of nutrients from food.
Food digestion time chart:
Different food items take different times for digestion. Digestion is also dependent on age and sex. Following is the time for digestion of different food items to be digested for an adult.
Food | Digestion time |
Fruits | 30-40 minutes |
Vegetables | 60 minutes |
Fish | 5-8 Hours |
Meat | 3-4 hours |
Juices | 25-30 minutes |
Any mixed or fried food | 8 Hours |
How to speed up digestion:
In this sedentary and fast-moving lifestyle, everyone experiences digestion problems such as gas, stomach upset, constipation, diarrhea, and heartburn. These symptoms can be rectified or improved by improving the eating habits. How to improve digestion? It is a common question that comes into every person’s mind. Digestion can be improved by the below steps.
Include fibrous food in to daily diet.
Add omega-3 fatty acids to your daily diet plan.
Drink at least 2-3 liters of water a day.
Stay stress-free.
Eat your food slowly and patiently.
Chew your bite at least 32 times.
Do regular exercise.
Quite smoking, alcohol, late-night eating.
Take at least 8 hours of sleep.
Avoid junk food and eat a balanced healthy diet.
A digestion specialist, a gastroenterologist, is a doctor who specializes in the digestive system and related diseases. The digestive system includes all the organs of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to rectum including the esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, large intestine, and small intestine.
Conclusion:
Proper digestion is a must for living a healthy and disease-free life. One should follow the proper diet plan and do regular exercise. Although Hydrochloric acid and enzymes are important for digestion eating fiber-rich food and avoiding bad cholesterol is also important for the body to work smoothly. Finally, avoid bad habits and adopt good ones as they both impact our digestion system in the reverse direction.
Image Source: Freepik